Tick‐borne encephalitis virus and LIV transmission involves a complex
Von einem Mystery-Man-Autor
Last updated 19 mai 2024

Download scientific diagram | Tick‐borne encephalitis virus and LIV transmission involves a complex ecology of reservoir species, ticks and indicator species that support tick populations. Small vertebrates including rodents, insectivores, and wild carnivores serve as amplifying reservoirs, developing high titer viremia and transmitting to ticks. Ticks transmit transstadially through egg, larvae, nymph, and adults, and transmit to a wide variety of vertebrate species. Large mammals such as deer and livestock maintain tick populations and are susceptible to disease, but do not transmit back to ticks due to low virus load, short duration of viremia or a combination of the 2. They are considered indicator species because they are valuable sentinel species for disease and antibody prevalence. Humans and horses are considered accidental hosts because they are not involved in sustaining transmission or feeding tick populations from publication: European College of Equine Internal Medicine consensus statement on equine flaviviridae infections in Europe | Horses and other equids can be infected with several viruses of the family Flaviviridae, belonging to the genus Flavivirus and Hepacivirus. This consensus statement focuses on viruses with known occurrence in Europe, with the objective to summarize the current literature and | Flaviviridae, Hepacivirus and Internal Medicine | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

9 Tick-Borne Diseases and Their Symptoms - Tick-Borne Illnesses

Transmission, Tick-borne encephalitis

Tick-borne encephalitis - The Lancet

Tick borne encephalitis virus: An evolving threat - FasterCapital
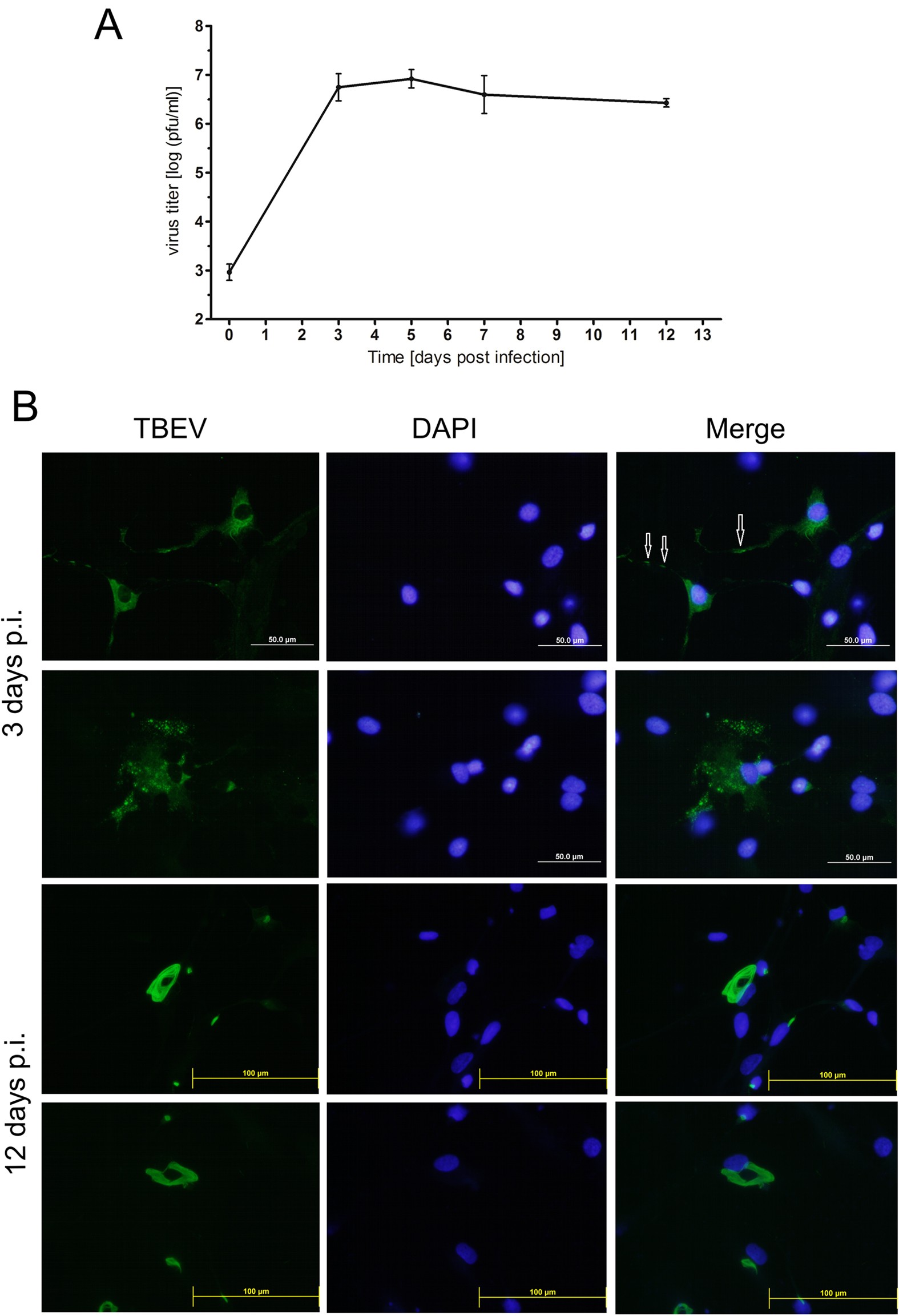
Electron Tomography Analysis of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus Infection in Human Neurons
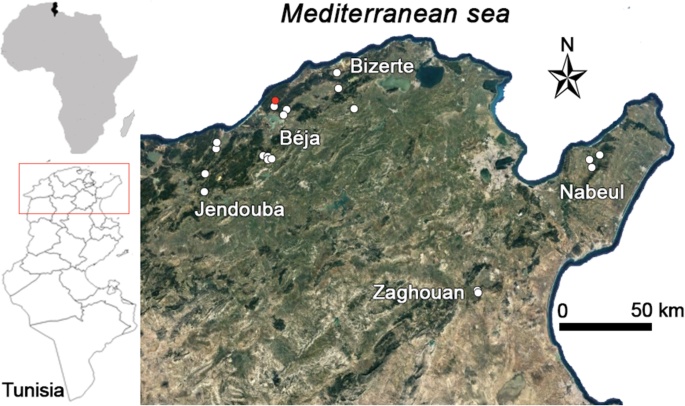
Presence of antibodies against tick-borne encephalitis virus in sheep in Tunisia, North Africa, BMC Veterinary Research

Life cycle of ixodid tick and transmission cycle of TBE virus. Black

The Challenges of Detecting Tick-Borne Diseases

TICKBORNE DISEASES OF THE UNITED STATES
für dich empfohlen
 Bussmann 2-Terminal 12 V. Flasher - Power Townsend Company14 Jul 2023
Bussmann 2-Terminal 12 V. Flasher - Power Townsend Company14 Jul 2023 FLASHER UNIT - UNIVERSAL 12V/300W MAX - 2 Terminals - for led/bulb flashers - FLOSSER ORIGINAL- - P2R14 Jul 2023
FLASHER UNIT - UNIVERSAL 12V/300W MAX - 2 Terminals - for led/bulb flashers - FLOSSER ORIGINAL- - P2R14 Jul 2023 Spatial patterns of enzymatic activity in large water bodies: Ship-borne measurements of beta-D-glucuronidase activity as a rapid indicator of microbial water quality - ScienceDirect14 Jul 2023
Spatial patterns of enzymatic activity in large water bodies: Ship-borne measurements of beta-D-glucuronidase activity as a rapid indicator of microbial water quality - ScienceDirect14 Jul 2023 VW Käfer Glühbirnen Blinker Orange 6V / 21W - Bekabo Classicparts14 Jul 2023
VW Käfer Glühbirnen Blinker Orange 6V / 21W - Bekabo Classicparts14 Jul 2023 Doppel 2 Faden Birne für Harley Davidson US Blinker gelb US Modell14 Jul 2023
Doppel 2 Faden Birne für Harley Davidson US Blinker gelb US Modell14 Jul 2023![Neofactory : 12V21W OEM Blinker Birne Silber [001441]](https://global-fs.webike-cdn.net/catalogue/images/115332/115332_L001441_TL.jpg) Neofactory : 12V21W OEM Blinker Birne Silber [001441]14 Jul 2023
Neofactory : 12V21W OEM Blinker Birne Silber [001441]14 Jul 2023 Blinker Birne, 12V 23W 1156 BA 15S (Paar) - Valkyrie Part's14 Jul 2023
Blinker Birne, 12V 23W 1156 BA 15S (Paar) - Valkyrie Part's14 Jul 2023![TANAKA TRADING : 12V Birnen Set Blinker Birne [ca0984]](https://global-fs.webike-cdn.net/catalogue/images/44098/984_TL.jpg) TANAKA TRADING : 12V Birnen Set Blinker Birne [ca0984]14 Jul 2023
TANAKA TRADING : 12V Birnen Set Blinker Birne [ca0984]14 Jul 2023 2x Chrom Silver Blinkerbirnen BAU15s Blinker Birnen Lampen Orange PY21W #314 Jul 2023
2x Chrom Silver Blinkerbirnen BAU15s Blinker Birnen Lampen Orange PY21W #314 Jul 2023 24V Blinker Birne im Rücklicht14 Jul 2023
24V Blinker Birne im Rücklicht14 Jul 2023
Sie können auch mögen
 Pomrone Spiegelabzieher Für Auto Rückspiegel, Rückspiegelwischer Einziehbarer -Mist-Spiegelwischer Autospiegelwischer -Mist-Spiegelwischer Glasreinigung Zubehör Für Autos: : Auto & Motorrad14 Jul 2023
Pomrone Spiegelabzieher Für Auto Rückspiegel, Rückspiegelwischer Einziehbarer -Mist-Spiegelwischer Autospiegelwischer -Mist-Spiegelwischer Glasreinigung Zubehör Für Autos: : Auto & Motorrad14 Jul 2023 Anniversary Car Decoration - Surprise Guys14 Jul 2023
Anniversary Car Decoration - Surprise Guys14 Jul 2023 Start Booster P4 Professional 12V 2500A portable starter14 Jul 2023
Start Booster P4 Professional 12V 2500A portable starter14 Jul 2023 Alpine Bike Works - Alpine Bike Works14 Jul 2023
Alpine Bike Works - Alpine Bike Works14 Jul 2023 Wasserkanister Camping 10 Liter QUECHUA - DECATHLON14 Jul 2023
Wasserkanister Camping 10 Liter QUECHUA - DECATHLON14 Jul 2023 1,5KE 10A: TVS-Diode, unidirektional, 8,55 V, 1500 W, DO-201 bei reichelt elektronik14 Jul 2023
1,5KE 10A: TVS-Diode, unidirektional, 8,55 V, 1500 W, DO-201 bei reichelt elektronik14 Jul 2023 1000W Netzgekoppelter Solar Wechselrichter, Grid Tie Inverter, MPPT Reine Sinuswellenausgabe Solar Netzgekoppelter Wechselrichter für PV-Panels14 Jul 2023
1000W Netzgekoppelter Solar Wechselrichter, Grid Tie Inverter, MPPT Reine Sinuswellenausgabe Solar Netzgekoppelter Wechselrichter für PV-Panels14 Jul 2023 Universal Auto vorne/hinten Seiten fenster Sonnenblende Schatten Netz abdeckung Auto UV-Schutz Vorhang Seiten fenster Sonnenschutz Mesh Kinder schutz - AliExpress14 Jul 2023
Universal Auto vorne/hinten Seiten fenster Sonnenblende Schatten Netz abdeckung Auto UV-Schutz Vorhang Seiten fenster Sonnenschutz Mesh Kinder schutz - AliExpress14 Jul 2023 Мембрана клапана картерних газів R58 Mini 1.6 1.8 06H103495A14 Jul 2023
Мембрана клапана картерних газів R58 Mini 1.6 1.8 06H103495A14 Jul 2023 Handtuch Auto Sitz Abdeckung Atmungsaktiv Polyester Terry Tuch Mit14 Jul 2023
Handtuch Auto Sitz Abdeckung Atmungsaktiv Polyester Terry Tuch Mit14 Jul 2023