Figure 2 from Understanding the fate of peroxynitrite in plant cells--from physiology to pathophysiology.
Von einem Mystery-Man-Autor
Last updated 07 Juni 2024

Fig. 2. A hypothetical regulatory mechanisms of ONOO action in plant cells. In the biological milieu the peroxynitrite anion (ONOO ) is in equilibrium with peroxynitrous acid (ONOOH; pKa = 6.8). The reaction of ONOO with carbon dioxide leads to the formation of carbonate (CO 3 ) and nitrogen dioxide ( NO2) radicals. Alternatively, ONOOH can undergo homolytic fission to generate one-electron oxidants, hydroxyl OH and NO2 radicals. ONOOH readily crosses lipid bilayers and its decomposition to OH and NO2 radicals seems to become relevant in hydrophobic phases to initiate lipid peroxidation and lipid and protein nitration processes. If ONOO combines with SH-containing molecules (X-SH), it might be converted to S-nitroso compounds, e.g. S-nitrosoglutathione. Nitration and the formation of S-nitroso compounds are proposed mechanisms, by which ONOO regulates NO-dependent signaling events. On the other hand, nucleotides within DNA and RNA can undergo nitration by ONOO forming 8-nitroguanine, which may impart pathological consequences (Corpas et al., 2009b). - "Understanding the fate of peroxynitrite in plant cells--from physiology to pathophysiology."

Reactive Oxygen Species: Physiological and Physiopathological

Frataxin deficiency disrupts mitochondrial respiration and
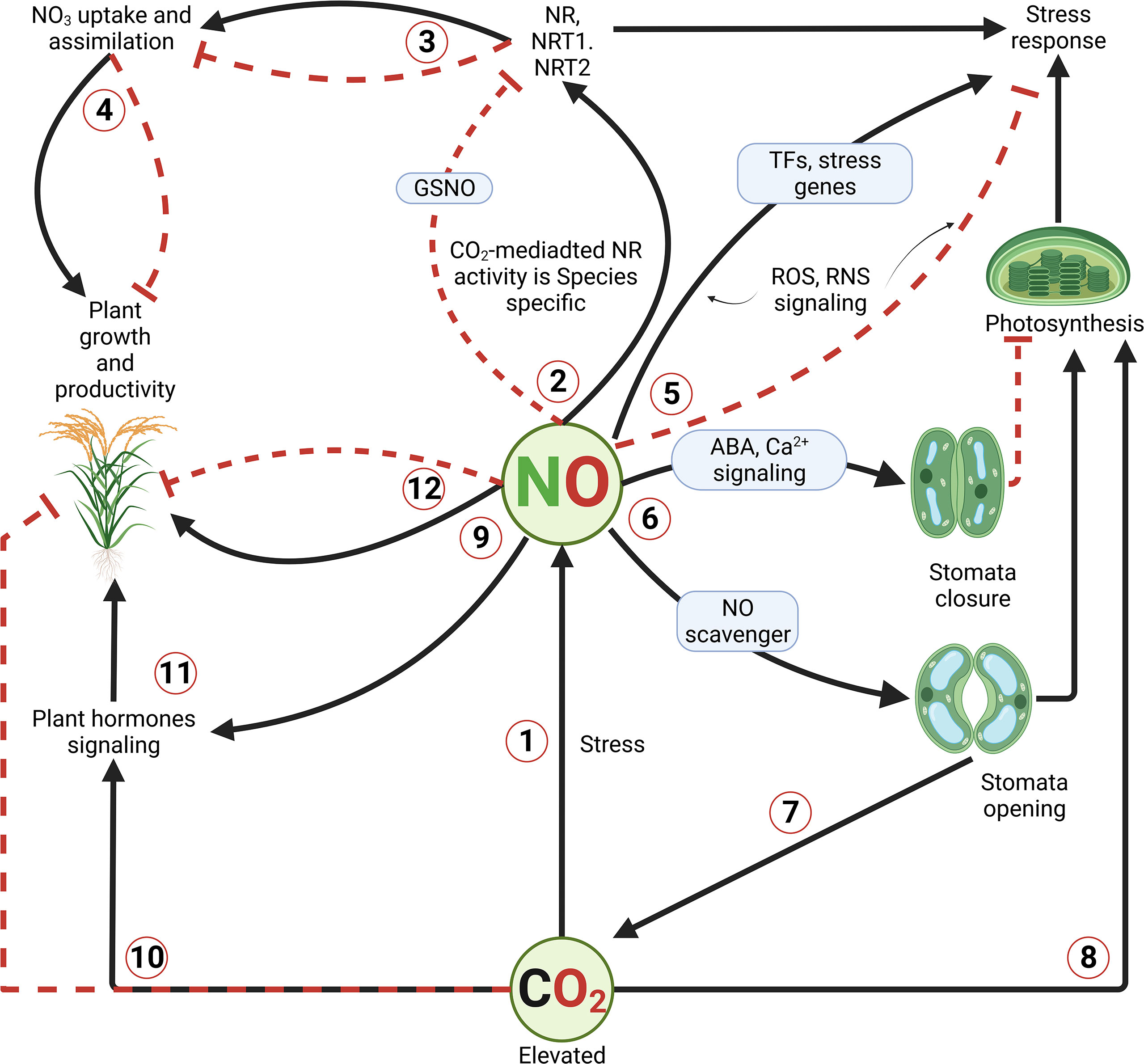
Frontiers Nitric oxide: A core signaling molecule under elevated
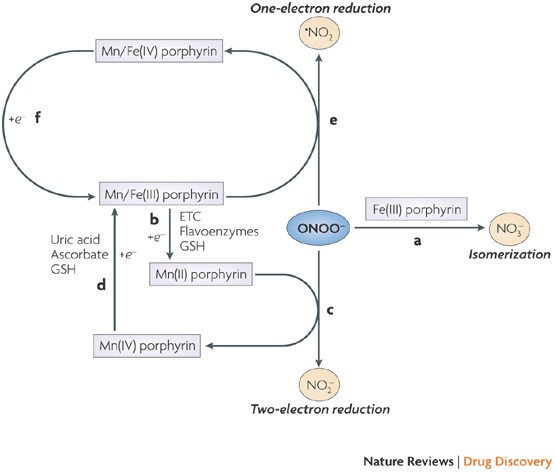
Peroxynitrite: biochemistry, pathophysiology and development of
Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. - Document

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Understanding the fate of peroxynitrite in plant cells – From

Full article: Plumbagin attenuated oxygen-glucose deprivation

Reactive Oxygen Species: Physiological and Physiopathological

Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease

Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease
für dich empfohlen
 Conversion of •NO and ONOO − . Activated macrophages simultaneously14 Jul 2023
Conversion of •NO and ONOO − . Activated macrophages simultaneously14 Jul 2023 Affinity Studies of Hemicyanine Derived Water Soluble Colorimetric Probes with Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen/Sulfur Species - Ghosh - 2023 - ChemBioChem - Wiley Online Library14 Jul 2023
Affinity Studies of Hemicyanine Derived Water Soluble Colorimetric Probes with Reactive Oxygen/Nitrogen/Sulfur Species - Ghosh - 2023 - ChemBioChem - Wiley Online Library14 Jul 2023 Peroxynitrite (ONOO − ) formation from NO and superoxide anion (O 2 •−14 Jul 2023
Peroxynitrite (ONOO − ) formation from NO and superoxide anion (O 2 •−14 Jul 2023 IJMS, Free Full-Text14 Jul 2023
IJMS, Free Full-Text14 Jul 2023- Wrestlecon2024 is happy to announce Sonny Onoo! Brought to you by Woo Games.14 Jul 2023
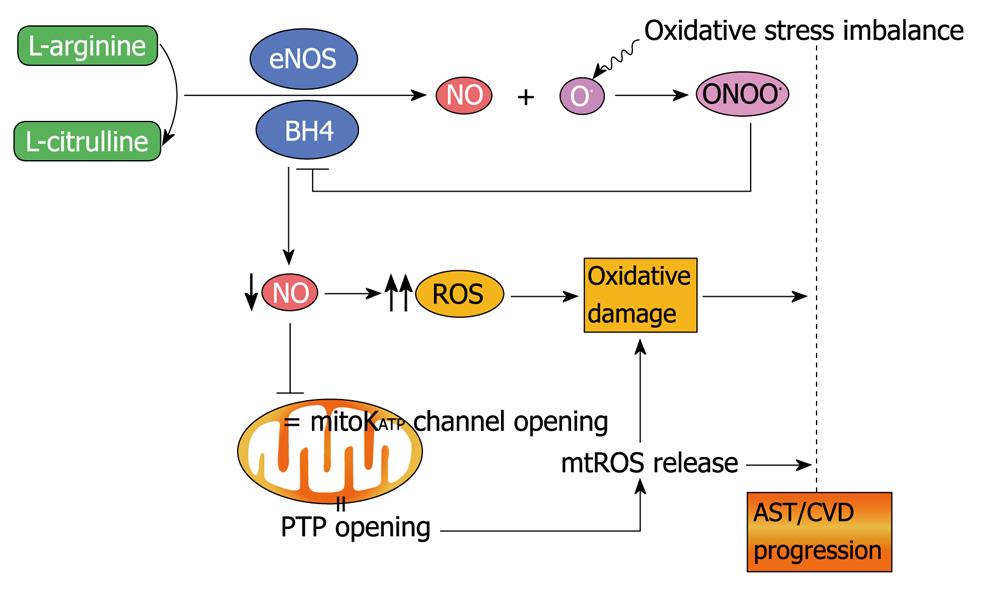 Regulatory role of mitochondria in oxidative stress and atherosclerosis14 Jul 2023
Regulatory role of mitochondria in oxidative stress and atherosclerosis14 Jul 2023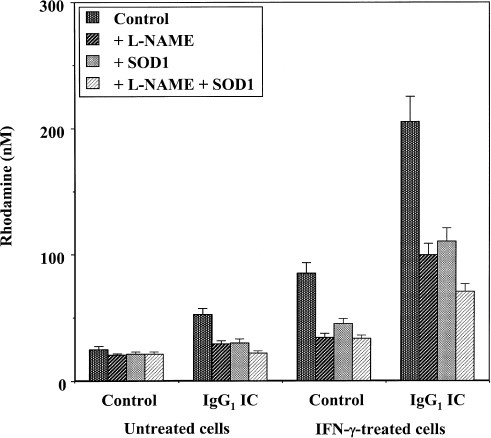 Fc-Receptor-Mediated Intracellular Delivery of Cu/Zn-superoxide Dismutase (SOD1) Protects Against Redox-Induced Apoptosis Through a Nitric Oxide Dependent Mechanism, Molecular Medicine14 Jul 2023
Fc-Receptor-Mediated Intracellular Delivery of Cu/Zn-superoxide Dismutase (SOD1) Protects Against Redox-Induced Apoptosis Through a Nitric Oxide Dependent Mechanism, Molecular Medicine14 Jul 2023 Peroxynitrite activates ERK via Raf-1 and MEK, independently from EGF receptor and p21Ras in H9C2 cardiomyocytes - Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology14 Jul 2023
Peroxynitrite activates ERK via Raf-1 and MEK, independently from EGF receptor and p21Ras in H9C2 cardiomyocytes - Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology14 Jul 2023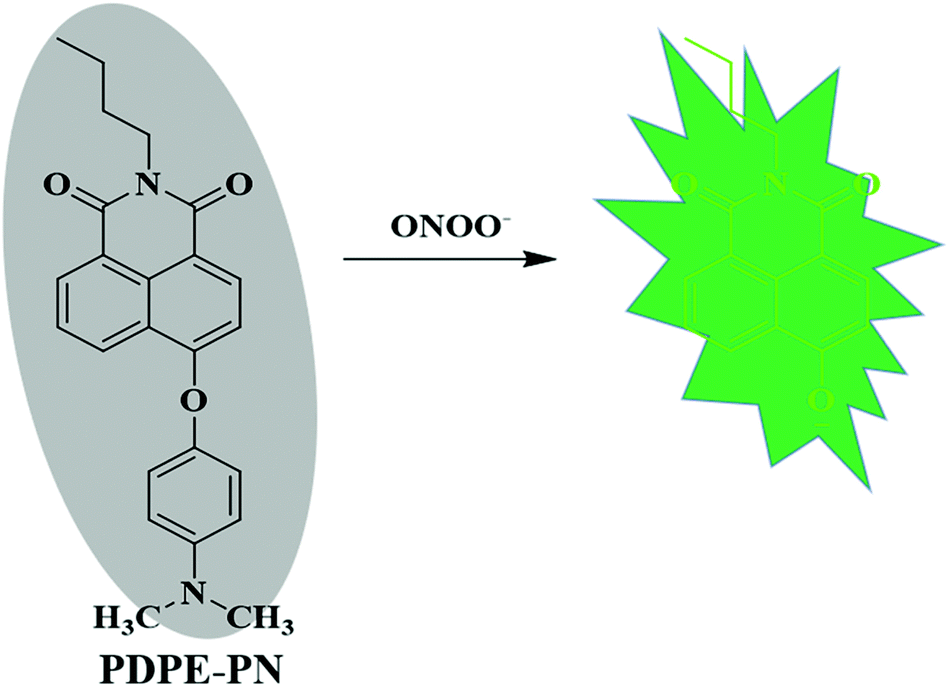 A novel p -dimethylaminophenylether-based fluorescent probe for the detection of native ONOO − in cells and zebrafish - Analyst (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1AN00608H14 Jul 2023
A novel p -dimethylaminophenylether-based fluorescent probe for the detection of native ONOO − in cells and zebrafish - Analyst (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1AN00608H14 Jul 2023 Peroxynitrite Inhibits Glutamate Transporter Subtypes (∗) - Journal of Biological Chemistry14 Jul 2023
Peroxynitrite Inhibits Glutamate Transporter Subtypes (∗) - Journal of Biological Chemistry14 Jul 2023
Sie können auch mögen
- Ausführungen Innentüren14 Jul 2023
 How to Pay for Abu Dhabi Parking Via SMS14 Jul 2023
How to Pay for Abu Dhabi Parking Via SMS14 Jul 2023 Car Back Seat Organizer with Foldable Tray Dining Tablet Holder14 Jul 2023
Car Back Seat Organizer with Foldable Tray Dining Tablet Holder14 Jul 2023 Wooden Full Drill Diamond Cup Coastesr Doughnut with Holder Sweet14 Jul 2023
Wooden Full Drill Diamond Cup Coastesr Doughnut with Holder Sweet14 Jul 2023 El Stroboskobu - Stroboskop14 Jul 2023
El Stroboskobu - Stroboskop14 Jul 2023 Spurtar Autofolie Schwarz Glänzend - 5CMx6M Selbstklebend Zierleisten Folie für Auto Motorrad Fenster Kfz Chromleisten Folierung (Schwarze Folie, 2in14 Jul 2023
Spurtar Autofolie Schwarz Glänzend - 5CMx6M Selbstklebend Zierleisten Folie für Auto Motorrad Fenster Kfz Chromleisten Folierung (Schwarze Folie, 2in14 Jul 2023 Here's why there isn't an iPhone 14 mini – and why there won't be14 Jul 2023
Here's why there isn't an iPhone 14 mini – and why there won't be14 Jul 2023 Flow.month Pet Front Seat Cover Pet Booster Seat,Deluxe 2 in 1 Dog Seat Cover for Cars Waterproof Dog Front Seat Cover Pet Bucket Seat Cover with14 Jul 2023
Flow.month Pet Front Seat Cover Pet Booster Seat,Deluxe 2 in 1 Dog Seat Cover for Cars Waterproof Dog Front Seat Cover Pet Bucket Seat Cover with14 Jul 2023 Ladekantenschutz Edelstahl MATT kompatibel für BMW X1 E84 2009-2012 vor LCI, mit Abkantung14 Jul 2023
Ladekantenschutz Edelstahl MATT kompatibel für BMW X1 E84 2009-2012 vor LCI, mit Abkantung14 Jul 2023 Mascherina anteriore nera con cornice cromata per countryman f60 2014 Jul 2023
Mascherina anteriore nera con cornice cromata per countryman f60 2014 Jul 2023
